原子操作类
1. 简介
原子类位于java.util.concurrent.atomic包下: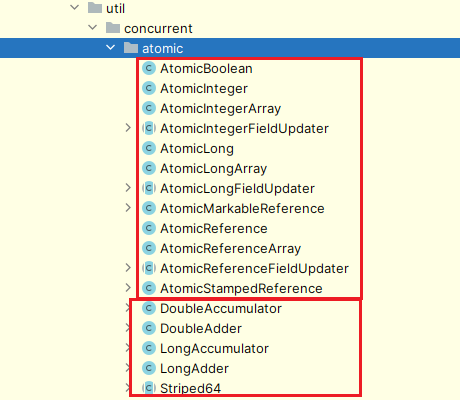 按照原子类的特性,可以分为:基本类型原子类、数组类型原子类、引用类型原子类、对象属性修改原子类、原子操作增强类。
按照原子类的特性,可以分为:基本类型原子类、数组类型原子类、引用类型原子类、对象属性修改原子类、原子操作增强类。
2. 基本类型原子类
AtomicBoolean、AtomicInteger、AtomicLong
2.1 常用的API

2.2 实操
public class AtomicBaseTypeDemo {
static class MyNumber{
public AtomicInteger number = new AtomicInteger(0);
public void addPlus(){
number.getAndIncrement();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
int values = 50;
MyNumber myNumber = new MyNumber();
CountDownLatch countDownLatch = new CountDownLatch(values);
for (int i = 0; i < values; i++) {
new Thread(()->{
try {
for (int j = 0; j < 100; j++) {
myNumber.addPlus();
}
}finally {
countDownLatch.countDown();
}
}).start();
}
countDownLatch.await();
System.out.println("结果是:"+myNumber.number.get());
}
}引入CountDownLatch是防止main线程提前结束,导致计算结果没有执行完毕就被结束。
3. 数组类型原子类
AtomicIntegerArray、AtomicLongArray、AtomicReferenceArray, api和基本类型差不多:
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
AtomicIntegerArray integerArray = new AtomicIntegerArray(new int[]{1, 4, 7});
System.out.println(integerArray.compareAndSet(1, integerArray.get(1), 8));
System.out.println(integerArray.getAndIncrement(0)+"更改后的值: "+integerArray.get(0));
}4. 引用类型原子类
AtomicReference、AtomicReferenceArray、AtomicStampedReference、AtomicMarkableReference,其中AtomicStampedReference、AtomicMarkableReference都用来解决ABA问题,区别是AtomicStampedReference可以记录被修改的次数,AtomicMarkableReference只记录是否被修改。
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
AtomicMarkableReference<String> markableReference = new AtomicMarkableReference<>("aaa", false);
new Thread(()->{
boolean marked = markableReference.isMarked();
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"==,修改标识:"+marked);
markableReference.compareAndSet("aaa", "bbb", false, true);
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"==,修改标识:"+markableReference.isMarked());
}, "t1").start();
new Thread(()->{
boolean marked = markableReference.isMarked();
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"==,修改标识:"+marked);
try {
Thread.sleep(20);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
boolean flag = markableReference.compareAndSet("aaa", "ccc", false, !marked);
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"==,是否修改成功:"+flag+", 当前修改标识:"+markableReference.isMarked());
}, "t2").start();
}运行结果: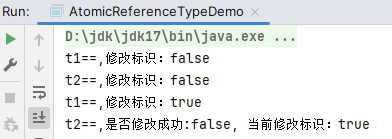
5. 对象属性修改原子类
AtomicIntegerFieldUpdater、AtomicLongFieldUpdater、AtomicReferenceFieldUpdater可以对被volatile修饰的变量进行原子级别的更新。主要用来操作更新非线程安全对象内的字段信息。
5.1 使用要求
- 更新的对象属性必须使用public volatile修饰符。
- 因为对象的属性修改类型原子类都是抽象类,所以每次使用都必须使用静态方法
newUpdater()创建一个更新器,并且需要设置想要更新的类和属性。
5.2 实操
public class AtomicFieldDemo {
static class Resource {
public volatile String filePath = "/tmp";
AtomicReferenceFieldUpdater<Resource, String> fieldUpdater =
AtomicReferenceFieldUpdater.newUpdater(Resource.class, String.class, "filePath");
public void updateFilePath(Resource resource){
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"\t"+"start change");
boolean flag = fieldUpdater.compareAndSet(resource, "/tmp", "/opt");
if(flag){
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"\t"+"处理完毕");
}else{
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"\t"+"其他线程已经处理过了");
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
Resource resource = new Resource();
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
new Thread(()->{
resource.updateFilePath(resource);
}, "t"+(i+1)).start();
}
}
}运行结果: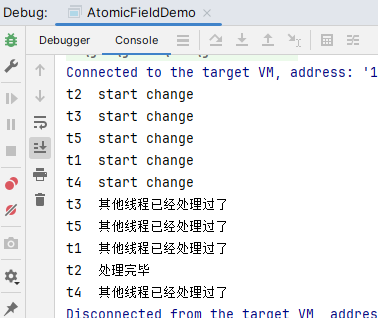
6. 原子操作增强类
DoubleAccumulator、DoubleAdder、LongAccumulator、LongAdder,他们都是Striped64的子类,他们是在jdk8开始提供的。参考阿里规范手册: LongAdder这些增强类在普通场景下和其他原子类性能差不多,但是在高并发场景下性能更好。其中LongAdder只能累加,LongAccumulator可以做自定义计算逻辑。
LongAdder这些增强类在普通场景下和其他原子类性能差不多,但是在高并发场景下性能更好。其中LongAdder只能累加,LongAccumulator可以做自定义计算逻辑。
6.1 常见api
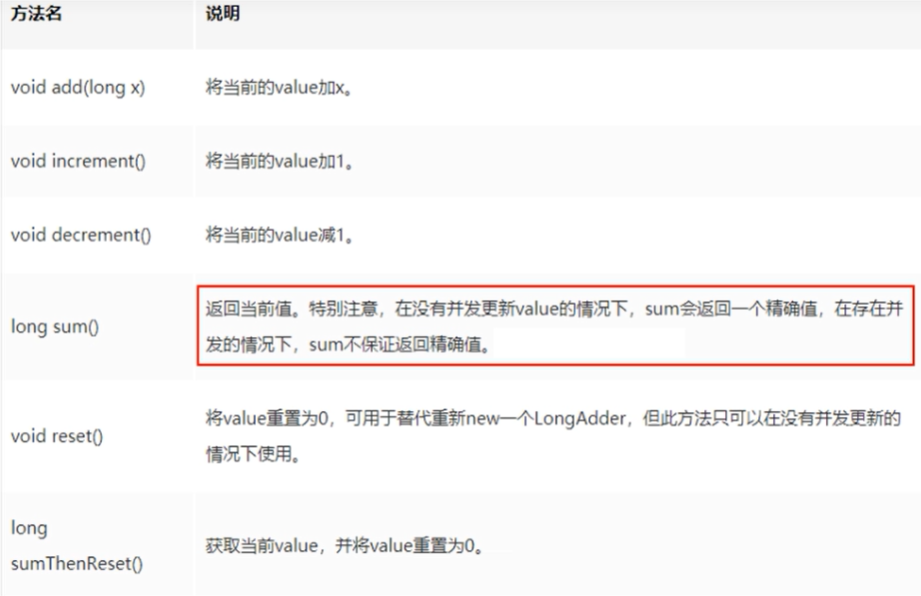
6.2 实操
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
LongAdder longAdder = new LongAdder();
longAdder.add(20);
longAdder.increment();
System.out.println(longAdder.sum());
// 传入计算逻辑,和初始值
LongAccumulator longAccumulator = new LongAccumulator((x, y)->x+y, 0);
longAccumulator.accumulate(123);
longAccumulator.accumulate(100);
System.out.println(longAccumulator.get());
}7. LongAdder的底层原理
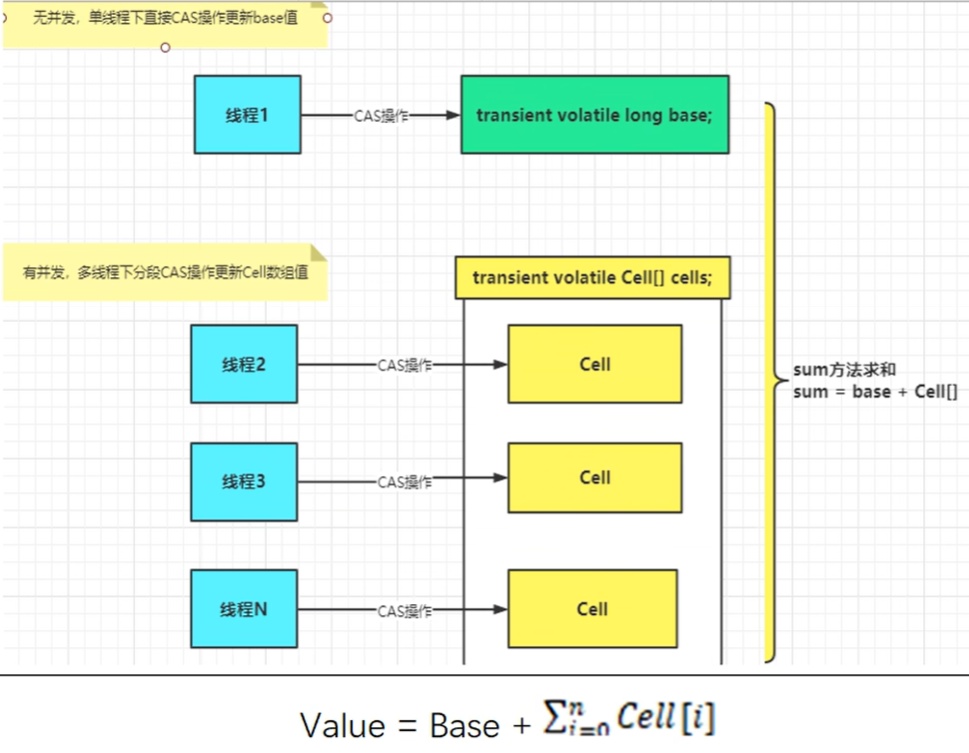
LongAdder的父类是Striped64。
7.1 Striped64属性方法
base:类似于AtomicLong中全局的value值。在没有竞争情况下数据直接累加到base上,或者cells扩容时,也需要将数据写入到base上。
colide:表示扩容意向,false一定不会扩容,true可能会扩容
celsBusy:初始化cells或者扩容cels需要获取锁,0:表示无锁状态 1:表示其他线程已经持有了锁。
casCellsBusy():通过CAS操作修改celsBusy的值,CAS成功代表获取锁,返回true
NCPU: 当前计算机CPU数量,Cell数组扩容时会使用到
getProbe():获取当前线程的hash值
advanceProbe():重置当前线程的hash值
7.2 LongAdder快的原理
LongAdder的基本思路就是分散热点,将vaue值分散到一个Cel数组中,不同线程会命中到数组的不同槽中,各个线程只对自己槽中的那个值进行CAS操作,这样热点就被分散了,冲突的概率就小很多。如果要获取真正的long值,只要将各个槽中的变量值累加返回。sum()会将所有Cel数组中的value和base累加作为返回值,核心的思想就是将之前AtomicLong一个value的更新压力分散到多个value中去, 从而降级更新热点。