集合的线程安全
1. ArrayList并非线程安全
public class NotSafeDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List list = new ArrayList();
// 多个线程同时对集合进行修改
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
new Thread(() ->{
list.add(UUID.randomUUID().toString().substring(0,6));
System.out.println(list);
}, "线程" + i).start();
}
}
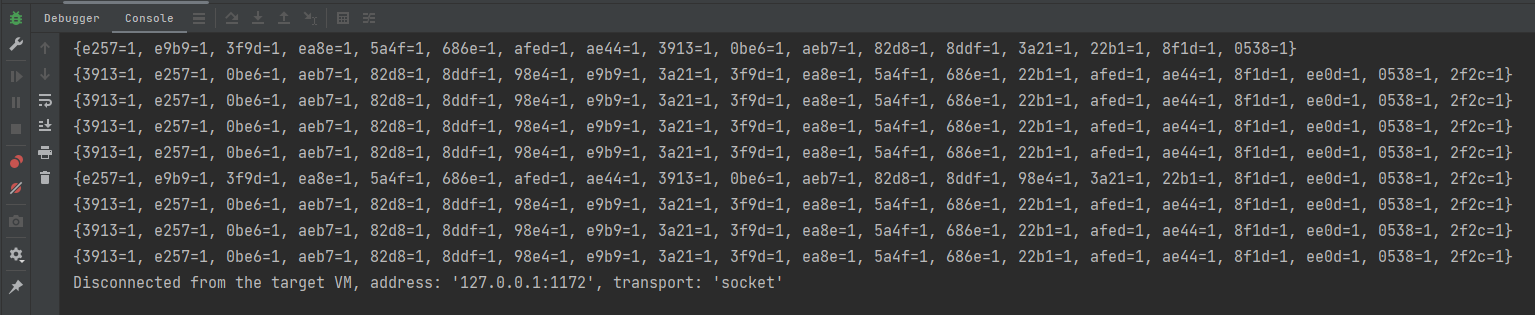
}运行结果: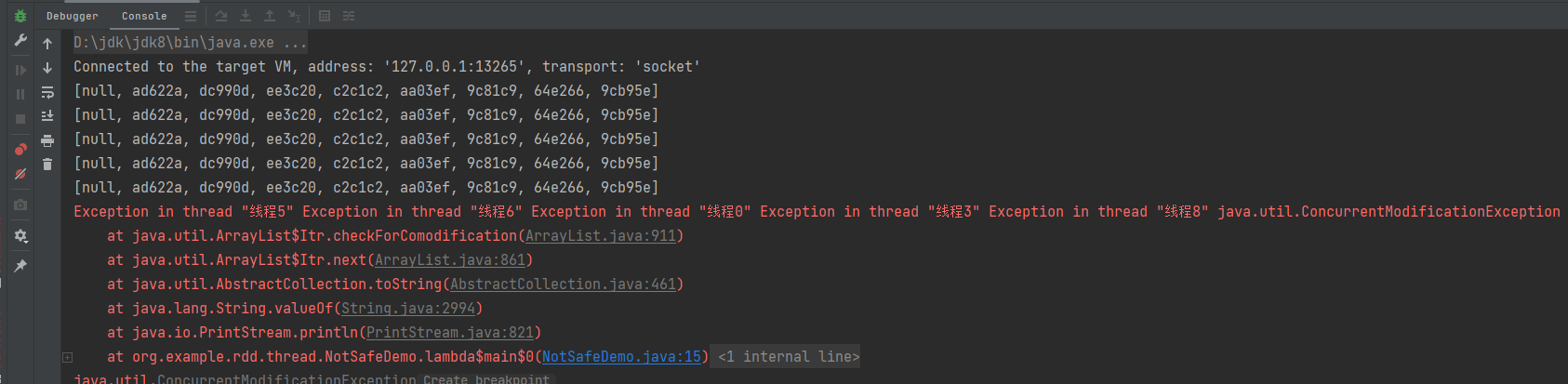 爆出异常
爆出异常ConcurrentModificationException的原因是ArrayList类的add方法不是线程安全的, 如果a线程在加数据,b线程在取数据 就会报错。
// 并没有锁机制
public boolean add(E e) {
ensureCapacityInternal(size + 1); // Increments modCount!!
elementData[size++] = e;
return true;
}2. 使用Vector
Vector 是矢量队列,它是JDK1.0版本添加的类。继承于AbstractList,实现了List, RandomAccess, Cloneable这些接口。Vector继承了AbstractList,实现了List;所以它是一个队列,支持相关的添加、删除、修改、遍历等功能。Vector实现了RandmoAccess接口,即提供了随机访问功能。 RandmoAccess是java中用来被List实现,为List提供快速访问功能的。在Vector中,我们即可以通过元素的序号快速获取元素对象;这就是快速随机访 问。Vector实现了Cloneable接口,即实现clone()函数。它能被克隆。 查看Vector的add方法:
public synchronized boolean add(E e) {
modCount++;
ensureCapacityHelper(elementCount + 1);
elementData[elementCount++] = e;
return true;
}add方法被synchronized同步修辞,线程安全!因此没有并发异常
3. Collections工具类
Collections提供了方法synchronizedList保证list是同步线程安全的。
public static void main(String[] args) {
List list = Collections.synchronizedList(new ArrayList<>());
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
new Thread(() -> {
list.add(UUID.randomUUID().toString().substring(0, 4));
System.out.println(list);
}, "线程" + i).start();
}
}其中synchronizedList方法源码:
public static <T> List<T> synchronizedList(List<T> list) {
return (list instanceof RandomAccess ?
new SynchronizedRandomAccessList<>(list) :
new SynchronizedList<>(list));
}4. CopyOnWriteArrayList
Vector和Collections.synchronizedList()都不是concurrent包下面的,JUC提供了线程安全类CopyOnWriteArrayList。
它相当于线程安全的ArrayList。和ArrayList 一样,它是个可变数组;但是和ArrayList不同的时,它具有以下特性:
- 它最适合于具有以下特征的应用程序:List 大小通常保持很小,只读操作远多于可变操作,需要在遍历期间防止线程间的冲突。
- 它是线程安全的。
- 因为通常需要复制整个基础数组,所以可变操作(
add()、set()和remove()等等)的开销很大。 - 迭代器支持
hasNext(),next()等不可变操作,但不支持可变remove()等操作。 - 使用迭代器进行遍历的速度很快,并且不会与其他线程发生冲突。在构造迭代器时,迭代器依赖于不变的数组快照。
public static void main(String[] args) {
List list = new CopyOnWriteArrayList();
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
new Thread(() -> {
list.add(UUID.randomUUID().toString().substring(0, 4));
System.out.println(list);
}, "线程" + i).start();
}
}对于集合的并发读写有三种实现思路:
- 独占锁, 缺点:效率低
- 采用读写分离思想解决, 缺点:写线程获取到锁,其他写线程阻塞
- 复制思想:
第二种思路还有一个问题: 就是数据不一致的问题。如果写线程还没来得及写会内存,其他的线程就会读到了脏数据。
CoypOnWriteArrayList的实现思路是第三种:当我们往一个容器添加元素的时候,不直接往当前容器添加,而是先将当前容器进行Copy,复制出一个新的容器,然后新的容器里添加元素,添加完元素之后,再将原容器的引用指向新的容器。
public boolean add(E e) {
final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;
lock.lock();
try {
Object[] elements = getArray();
int len = elements.length;
// 创建新数组
Object[] newElements = Arrays.copyOf(elements, len + 1);
// 新数组末尾添加元素
newElements[len] = e;
// 设置数组用新数组
setArray(newElements);
return true;
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}从"动态数组"和"线程安全"两个方面进一步对CopyOnWriteArrayList的原理进行说明:
- "动态数组"机制
- 它内部有个"volatile数组"(array)来保持数据。在"添加/修改/删除"数据时,都会新建一个数组,并将更新后的数据拷贝到新建的数组中,最后再将该数组赋值给"volatile 数组", 这就是它叫做 CopyOnWriteArrayList 的原因
- 由于它在"添加/修改/删除"数据时,都会新建数组,所以涉及到修改数据的操作,CopyOnWriteArrayList 效率很低;但是单单只是进行遍历查找的话,效率比较高。
- "线程安全"机制
- 通过volatile和互斥锁来实现的。
- 通过"volatile数组"来保存数据的。一个线程读取volatile数组时,总能看到其它线程对该volatile变量最后的写入;就这样,通过volatile提供了"读取到的数据总是最新的"这个机制的保证。
- 通过互斥锁来保护数据。在"添加/修改/删除"数据时,会先"获取互斥锁",再修改完毕之后,先将数据更新到"volatile 数组"中,然后再"释放互斥锁",就达到了保护数据的目的。
5. HashSet并非线程安全
public static void main(String[] args) {
Set set = new HashSet();
for (int i = 0; i < 20; i++) {
new Thread(() -> {
set.add(UUID.randomUUID().toString().substring(0, 4));
System.out.println(set);
}, "线程" + i).start();
}
}运行结果: 可见HashSet并不线程安全, HashSet的源码:
可见HashSet并不线程安全, HashSet的源码:
public boolean add(E e) {
return map.put(e, PRESENT)==null;
}add方法并没被Synchronized,也没有加上锁, 因此线程不安全。
6. CopyOnWriteArraySet
CopyOnWriteArraySet在concurrent包下在需要线程安全的场景下可以替换HashSet, CopyOnWriteArraySet底层实际就是通过CopyOnWriteArrayList来实现的,查看构造器源码: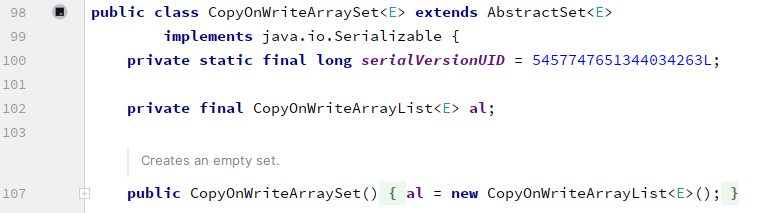 为了支持不重复的特性,在add()方法里面做了元素判断是否存在的:
为了支持不重复的特性,在add()方法里面做了元素判断是否存在的:
public boolean add(E e) {
return al.addIfAbsent(e);
}
// 实际调用的是CopyOnWriteArrayList的addIfAbsent方法
public boolean addIfAbsent(E e) {
Object[] snapshot = getArray();
// 满足不存在元素才进行添加
return indexOfRange(e, snapshot, 0, snapshot.length) < 0
&& addIfAbsent(e, snapshot);
}7. HashMap并非线程安全
public static void main(String[] args) {
HashMap map = new HashMap();
for (int i = 0; i < 20; i++) {
new Thread(() -> {
map.put(UUID.randomUUID().toString().substring(0, 4), "1");
System.out.println(map);
}, "线程" + i).start();
}
}运行结果: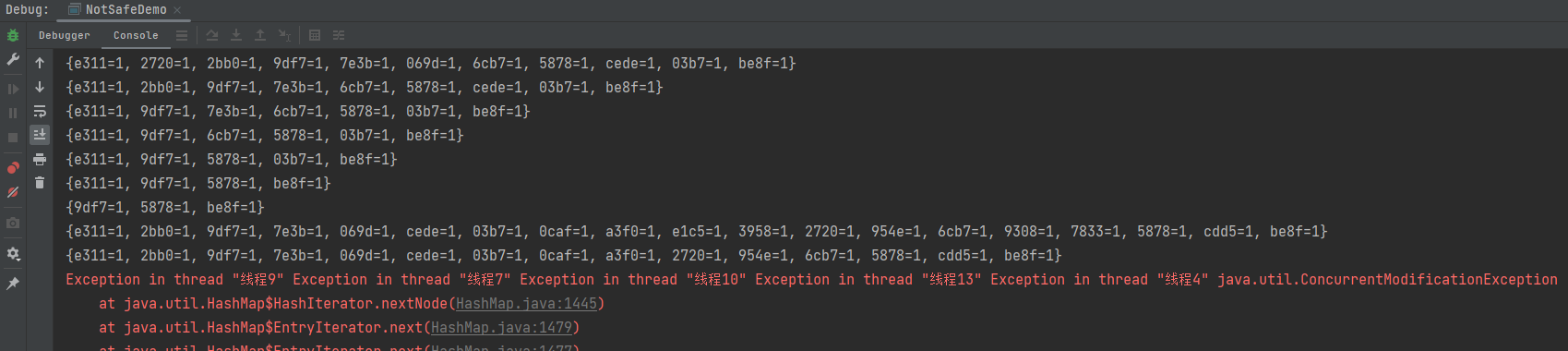
8. ConcurrentHashMap
public static void main(String[] args) {
ConcurrentHashMap map = new ConcurrentHashMap();
for (int i = 0; i < 20; i++) {
new Thread(() -> {
map.put(UUID.randomUUID().toString().substring(0, 4), "1");
System.out.println(map);
}, "线程" + i).start();
}
}