Channel
Java NIO中最重要的Channel的实现:
- FileChannel 从文件中读写数据。
- DatagramChannel 能通过 UDP 读写网络中的数据。
- SocketChannel 能通过 TCP 读写网络中的数据。
- ServerSocketChannel 可以监听新进来的 TCP 连接,像 Web 服务器那样。对每一个新进来的连接都会创建一个 SocketChannel。
正如你所看到的,这些通道涵盖了UDP和TCP网络IO,以及文件IO
1. FileChannel
FileChannel类可以实现常用的read,write以及scatter/gather操作,同时它也提供了很多专用于文件的新方法。
1.1 读取文件
操作步骤:
- FileChannel是一个接口,需要通过使用一个InputStream、OutputStream或RandomAccessFile来获取FileChannel实例
- 分配一个Buffer
- FileChannel调用read()把数据读到Buffer, read()方法返回的int值表示了有多少字节被读到了Buffer中。如果返回-1,表示到了文件末尾。
- 用完FileChannel后必须将其关闭。
FileChannel读取数据到Buffer中的示例:
// 创建FileChanel
RandomAccessFile aFile = new RandomAccessFile("C:\\Users\\mi\\Downloads\\鬼吹灯上.txt", "rw");
FileChannel inChannel = aFile.getChannel();
// 创建Buffer
ByteBuffer buf = ByteBuffer.allocate(48);
// 读取数据到buffer
int bytesReads = inChannel.read(buf);
while (bytesReads!=-1){
System.out.println("读取: "+bytesReads);
// 反转读写模式
buf.flip();
while (buf.hasRemaining()){
System.out.println(buf.get());
}
// 调用 buffer.clear() 或 buffer.compact() 清除缓冲区内容
buf.clear();
bytesReads = inChannel.read(buf);
}
aFile.close();
System.out.println("操作结束");1.2 向FileChannel写数据
操作步骤:
- FileChannel是一个接口,需要通过使用一个InputStream、OutputStream或RandomAccessFile来获取FileChannel实例
- 分配一个Buffer
- 清理Buffer, 将数据放入Buffer
- FileChannel.write()将Buffer数据写到文件中
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
// 创建FileChanel
FileOutputStream aFile = new FileOutputStream("C:\\Users\\mi\\Downloads\\demo.txt");
FileChannel outChannel = aFile.getChannel();
String strData = " fjsdlfjsdjfsdff fsdfsdfsdfjf;sdf;s sfsdfsd ";
// 创建Buffer
ByteBuffer buf = ByteBuffer.allocate(48);
// 读取数据到buffer
buf.clear();
buf.put(strData.getBytes());
// 反转读写模式
buf.flip();
while(buf.hasRemaining()) {
outChannel.write(buf);
}
outChannel.close();
System.out.println("操作结束");
}提示
FileChannel.write()是在while循环中调用的。因为无法保证write()方法一次能向FileChannel写入多少字节,因此需要重复调用write()方法,直到 Buffer 中已经没有尚未写入通道的字节
1.3 某个特定位置读/写
需要某个特定位置进行数据的读/写操作, 可以通过调用position()方法获取FileChannel的当前位置。也可以通过调用 position(long pos)方法设置FileChannel的当前位置。
long pos = channel.position();
channel.position(pos +123); // 当前位置向后移动123进行读写操作如果将位置设置在文件结束符之后,然后试图从文件通道中读取数据,读方法将返回- 1 (文件结束标志)。 如果将位置设置在文件结束符之后,然后向通道中写数据,文件将撑大到当前位置并写入数据。这可能导致"文件空洞",磁盘上物理文件中写入的数据间有空隙。
空洞文件的两个应用场景:
- 在使用迅雷下载文件时,还未下载完成,就发现该文件已经占据了全部文件大小的空间,这也是空洞文件;下载时如果没有空洞文件,多线程下载时文件就只能从一个地方写入,这就不能发挥多线程的作用了;如果有了空洞文件,可以从不同的地址同时写入,就达到了多线程的优势;
- 在创建虚拟机时,你给虚拟机分配了 100G 的磁盘空间,但其实系统安装完成之后,开始也不过只用了 3、4G 的磁盘空间,如果一开始就把 100G 分配出去,资源是很大的浪费。
1.4 获取文件大小
// 获取文件大小
long fileSize = outChannel.size();1.5 截取文件
可以使用 FileChannel.truncate()方法截取一个文件。截取文件时,文件将中指定长度后面的部分将被删除。如:
channel.truncate(1024); //截取文件的前1024个字节1.6 强制写到磁盘
FileChannel.force()方法将通道里尚未写入磁盘的数据强制写到磁盘上。出于性能方面的考虑,操作系统会将数据缓存在内存中,所以无法保证写入到 FileChannel里的数据一定会即时写到磁盘上。要保证这一点,需要调用 force()方法。force()方法有一个 boolean 类型的参数,指明是否同时将文件元数据(权限信息等)写到磁盘上。
1.7 通道之间的数据传输
如果两个通道中有一个是 FileChannel,那你可以直接将数据从一个channel传输到另外一个channel。
- transferFrom(): 可以将数据从源通道传输到FileChannel中
- transferTo()方法: transferTo()方法将数据从FileChannel传输到其他的channel中。
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
RandomAccessFile aFile = new RandomAccessFile("C:\\Users\\mi\\Downloads\\aa.txt", "rw");
FileChannel fromChannel = aFile.getChannel();
RandomAccessFile bFile = new RandomAccessFile("C:\\Users\\mi\\Downloads\\bb.txt", "rw");
FileChannel toChannel = bFile.getChannel();
long size = fromChannel.size();
// 直接覆盖
// toChannel.transferFrom(fromChannel, 0 , size);
// 两个文件合并, 起始位置若是toChannel.size()+1,将有一个未知字符
toChannel.transferFrom(fromChannel, toChannel.size() , size);
toChannel.close();
fromChannel.close();
System.out.println("over");
}2. ServerSocketChannel
ServerSocketChannel负责监听传入的连接和创建新的SocketChannel对象,它本身从不传输数据, 也就是本身不实现读和写功能。 ServerSocketChannel是一个基于通道的socket监听器,和java.net.ServerSocket作用一样,但额外支持非阻塞下运行。
public class ServerSocketChannelDemo {
public static final String GREETING = "Hello java nio.\r\n";
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
// 打开 ServerSocketChannel
ServerSocketChannel ssc = ServerSocketChannel.open();
ServerSocket serverSocket = ssc.socket();
// 服务端绑定8090端口
serverSocket.bind(new InetSocketAddress(8090));
// 设置为非阻塞模式
ssc.configureBlocking(false);
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.wrap(GREETING.getBytes());
while (true){
System.out.println("等待客户端连接================");
// 监听新的连接,返回一个包含新进来的连接的 SocketChannel。
// 在非阻塞模式下,如果没有连接进来, 立即返回null。
SocketChannel socketChannel = ssc.accept();
if(socketChannel==null){
System.out.println("服务器休息2S。。。。。");
Thread.sleep(2000);
}else {
// 获取远程连接地址
System.out.println("Incoming connection from: " + socketChannel.socket().getRemoteSocketAddress());
// 读取Buffer 中的所有数据,rewind将读取开始位置设为0
buffer.rewind();
socketChannel.write(buffer);
socketChannel.close();
}
}
}
}cmd窗口输入: telent 127.0.0.1 8090, 运行结果: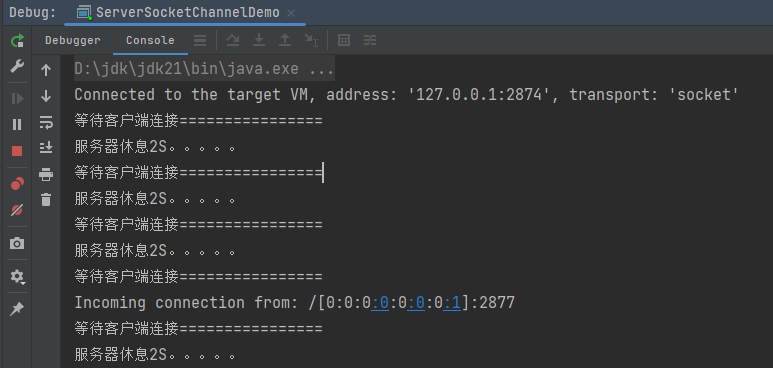 客户端接收到服务端返回消息
客户端接收到服务端返回消息 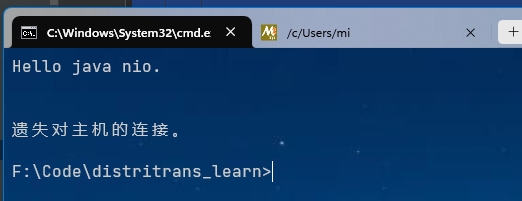
3. SocketChannel
Java NIO中的SocketChannel是一个连接到TCP网络套接字的通道,主要用途用来处理网络I/O的通道。SocketChannel可以被多路复用。
3.1 SocketChannel特点
- 对于已经存在的socket不能创建SocketChannel
- SocketChannel中提供的open接口创建的Channel并没有进行网络级联,需要使用connect接口连接到指定地址
- 未进行连接的SocketChannle执行I/O操作时,会抛出
NotYetConnectedException - SocketChannel支持两种I/O模式:阻塞式和非阻塞式
- SocketChannel 支持异步关闭。如果SocketChannel在一个线程上read阻塞,另一个线程对该SocketChannel调用
shutdownInput,则读阻塞的线程将返回-1 表示没有读取任何数据;如果SocketChannel在一个线程上write阻塞,另一个线程对该SocketChannel调用shutdownWrite,则写阻塞的线程将抛出AsynchronousCloseException - SocketChannel 支持设定参数:
- SO_SNDBUF 套接字发送缓冲区大小
- SO_RCVBUF 套接字接收缓冲区大小
- SO_KEEPALIVE 保活连接
- O_REUSEADDR 复用地址
- SO_LINGER 有数据传输时延缓关闭Channel(只有在非阻塞模式下有用)
- TCP_NODELAY 禁用Nagle算法
3.2 SocketChannel的使用
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
// 创建 SocketChannel
// 方式一
// SocketChannel socketChanne2 = SocketChannel.open();
// socketChanne2.connect(new InetSocketAddress("www.baidu.com", 80));
// 方式二
SocketChannel socketChannel = SocketChannel.open(new InetSocketAddress("www.sina.com", 80));
boolean open = socketChannel.isOpen();// 测试 SocketChannel 是否为 open 状态
System.out.println("=======open============" + open);
boolean connected = socketChannel.isConnected();//测试 SocketChannel 是否已经被连接
System.out.println("=========connected==========" + connected);
boolean connectionPending = socketChannel.isConnectionPending();//测试 SocketChannel 是否正在进行连接
System.out.println("========connectionPending===========" + connectionPending);
boolean finishConnect = socketChannel.finishConnect();//校验正在进行套接字连接的 SocketChannel是否已经完成连接
System.out.println("=========finishConnect==========" + finishConnect);
socketChannel.configureBlocking(false);
ByteBuffer byteBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(32);
socketChannel.read(byteBuffer);
Boolean keepAlive = socketChannel.getOption(StandardSocketOptions.SO_KEEPALIVE);
Integer soRcvbuf = socketChannel.getOption(StandardSocketOptions.SO_RCVBUF);
// 反转读写模式
byteBuffer.flip();
while(byteBuffer.hasRemaining()) {
System.out.println(byteBuffer.get());
}
socketChannel.close();
System.out.println("read over");
System.out.println(keepAlive);
System.out.println(soRcvbuf);
}4. DatagramChannel
使用DatagramChannel来处理UDP的数据传输。和TCP不同,UDP不是面向连接的协议。使用UDP时,只要知道服务器的IP和端口就可以直接向对方发送数据。
@Test
public void testClient() throws IOException {
// 打开 DatagramChannel
DatagramChannel receiveChannel = DatagramChannel.open();
//设置为非阻塞模式
receiveChannel.configureBlocking(false);
receiveChannel.bind(new InetSocketAddress(10086));
ByteBuffer receiveBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(512);
while (true) {
receiveBuffer.clear();
// 通过 receive()接收 UDP 包
SocketAddress receiveAddr = receiveChannel.receive(receiveBuffer);
receiveBuffer.flip();
System.out.print(receiveAddr.toString() + " ");
System.out.println(Charset.forName("UTF-8").decode(receiveBuffer));
}
}
@Test
// 发送数据
public void testServer() throws IOException, InterruptedException {
// 打开 DatagramChannel
DatagramChannel server = DatagramChannel.open();
//设置为非阻塞模式
server.configureBlocking(false);
while (true){
// 通过 send()发送 UDP 包
server.send(ByteBuffer.wrap("server msg: send".getBytes()), new InetSocketAddress("127.0.0.1",10086));
System.out.println("发包端发包");
Thread.sleep(1000);
}
}