CompletableFuture
1. CompletableFuture简介
CompletableFuture 在Java里面被用于异步编程,异步通常意味着非阻塞,可以使得我们的任务单独运行在与主线程分离的其他线程中,并且通过回调可以在主线程中得到异步任务的执行状态,是否完成和是否异常等信息。CompletableFuture实现了Future, CompletionStage接口,实现了Future接口就可以兼容现在有线程池框架,而CompletionStage接口才是异步编程的接口抽象,里面定义多种异步方法,通过这两者集合,从而打造出了强大的CompletableFuture类。
2. Future与CompletableFuture
Futrue在Java里面,通常用来表示一个异步任务的引用,比如我们将任务提交到线程池里面,然后我们会得到一个 Futrue,在Future里面有isDone方法来判断任务是否处理结束,还有get方法可以一直阻塞直到任务结束然后获取结果,但整体来说这种方式,还是同步的,因为需要客户端不断阻塞等待或者不断轮询才能知道任务是否完成。
Future的主要缺点如下:
- 不支持手动完成
我提交了一个任务,但是执行太慢了,我通过其他路径已经获取到了任务结果,现在没法把这个任务结果通知到正在执行的线程,所以必须主动取消或者一直等待它执行完成 - 不支持进一步的非阻塞调用
通过Future的get方法会一直阻塞到任务完成,但是想在获取任务之后执行额外的任务,因为 Future 不支持回调函数,所以无法实现这个功能 - 不支持链式调用
对于Future的执行结果,我们想继续传到下一个Future处理使用,从而形成一个链式的pipline调用,这在Future中是没法实现的。 - 不支持多个Future合并
比如我们有10个Future并行执行,我们想在所有的Future运行完毕之后,执行某些函数,是没法通过Future实现的。 - 不支持异常处理
Future的API没有任何的异常处理的api,所以在异步运行时,如果出了问题是不好定位的。
3. CompletableFuture入门
3.1 没有返回值的异步任务
使用runAsync()方法调用
java
// 异步线程没有返回结果
CompletableFuture<Void> completableFuture1 = CompletableFuture.runAsync(() -> {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"异步计算1");
});
completableFuture1.get();运行结果: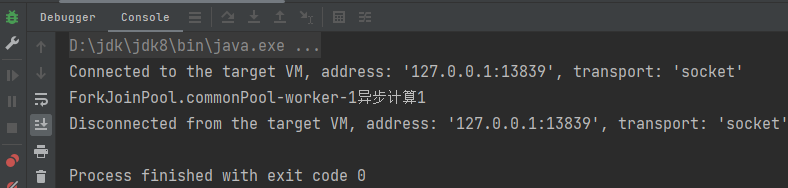
3.2 有返回值的异步任务
java
CompletableFuture<String> completableFuture2 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "异步计算2");
return "1024";
});
completableFuture2.whenComplete((result, exception)->{
System.out.println("计算结果: "+result);
System.out.println("计算异常: "+exception);
});运行结果: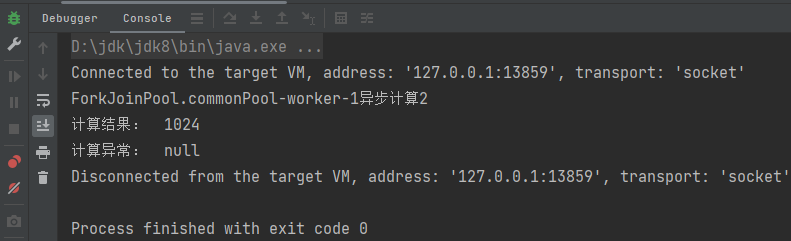
3.3 线程依赖
当一个线程依赖另一个线程时,可以使用thenApply方法来把这两个线程串行化。
java
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
CompletableFuture<String> completableFuture = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "异步计算");
return "2024";
}).thenApply(result -> {
// 上一步结果作为输入
return result + ", jiebaba";
});
String result = completableFuture.get();
System.out.println("最终计算结果为: " + result);
}运行结果: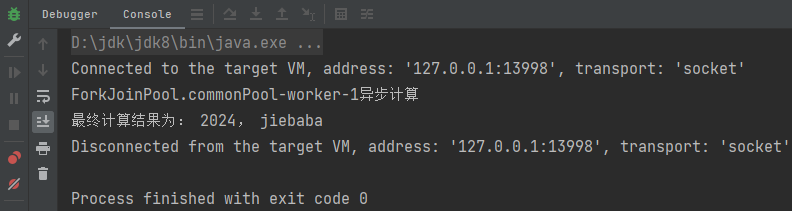
3.4 消费处理结果
thenAccept消费处理结果, 接收任务的处理结果,并消费处理,无返回结果。
java
private static int num = 0;
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
System.out.println("主线程开始");
CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
try {
System.out.println("加 10 任务开始");
num += 10;
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return num;
}).thenApply(integer -> {
return num * num;
}).thenAccept(new Consumer<Integer>() {
@Override
public void accept(Integer integer) {
System.out.println("子线程全部处理完成,最后调用了 accept,结果为:" +
integer);
}
});
}运行结果为: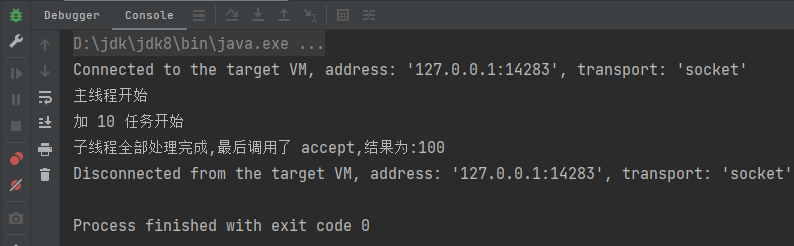
3.5 异常处理
exceptionally异常处理,出现异常时触发。
java
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
CompletableFuture<String> completableFuture = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "异步计算");
int i = 1 / 0;
return "2024";
}).exceptionally(ex -> {
System.out.println(ex.getMessage());
return "error";
});
String result = completableFuture.get();
System.out.println("最终计算结果为: " + result);
}运行结果为: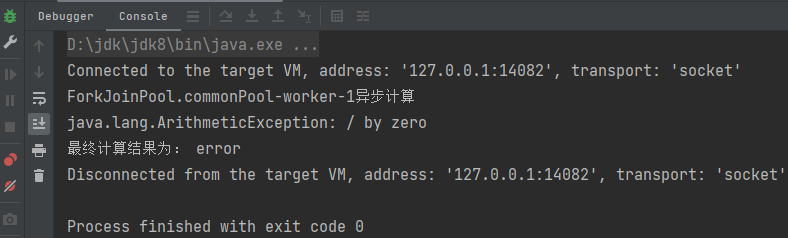
3.6 结果合并
thenCompose合并两个有依赖关系的CompletableFutures的执行结果
java
private static int num = 0;
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
System.out.println("主线程开始");
//第一步加 10
CompletableFuture<Integer> future = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println("加 10 任务开始");
num += 10;
return num;
});
//合并
CompletableFuture<Integer> future1 = future.thenCompose(i ->
//再来一个 CompletableFuture
CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
return i + 1;
}));
System.out.println(future.get());
System.out.println(future1.get());
}运行结果: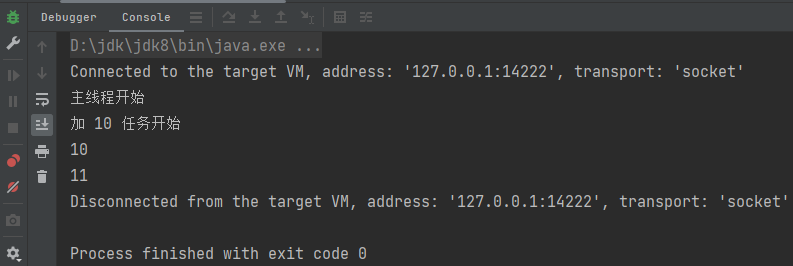
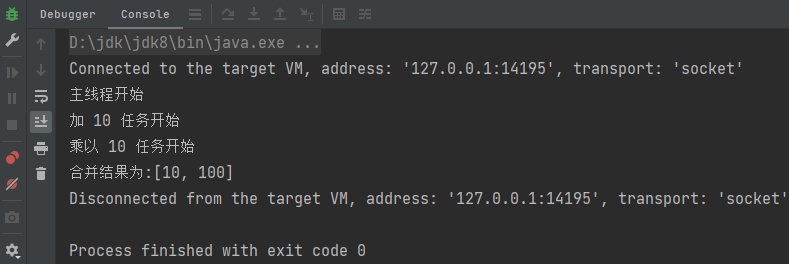
thenCombine合并两个没有依赖关系的CompletableFutures任务。
java
private static int num = 0;
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
System.out.println("主线程开始");
CompletableFuture<Integer> job1 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println("加 10 任务开始");
num += 10;
return num;
});
CompletableFuture<Integer> job2 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println("乘以 10 任务开始");
num = num * 10;
return num;
});
//合并两个结果
CompletableFuture<Object> future = job1.thenCombine(job2, new
BiFunction<Integer, Integer, List<Integer>>() {
@Override
public List<Integer> apply(Integer a, Integer b) {
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add(a);
list.add(b);
return list;
}
});
System.out.println("合并结果为:" + future.get());
}运行结果: